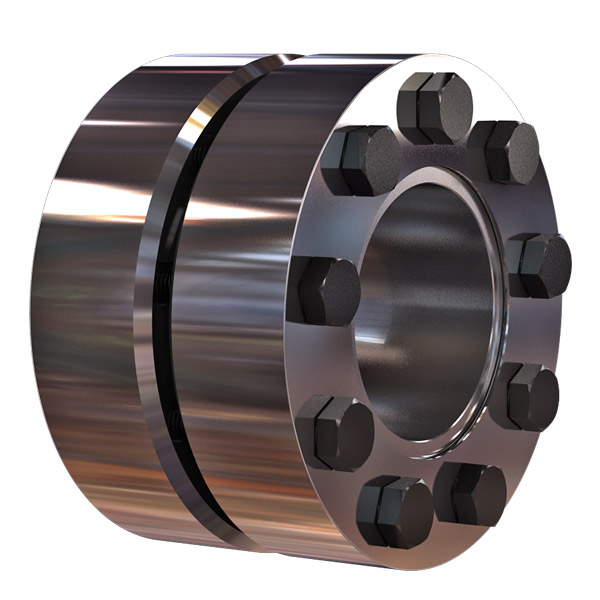
Product Description
Aluminum Stainless Disc Flexible Beam Coupling Encoder Coupling
| Material | Zinc Alloy a& Stainless steel 304 |
| Finish | Bright Black Plated |
| Features | With force telescopic function,suitable for different spigot height |
| Samples | Accepted |
Aluminum Stainless Disc Flexible Beam Coupling Encoder Coupling
| Stainless Steel Toggle Latch Clasp LATCH | |
Aluminum plum couplings D25L30 flexible jaw spider shaft coupler motor shaft coupling
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
Jaw Coupling Plum Coupling Elastic Coupling
Jaw Coupling Plum Coupling Elastic Coupling
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
Pto Shafts Flexible Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Coupling Transmission Part Couplings
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
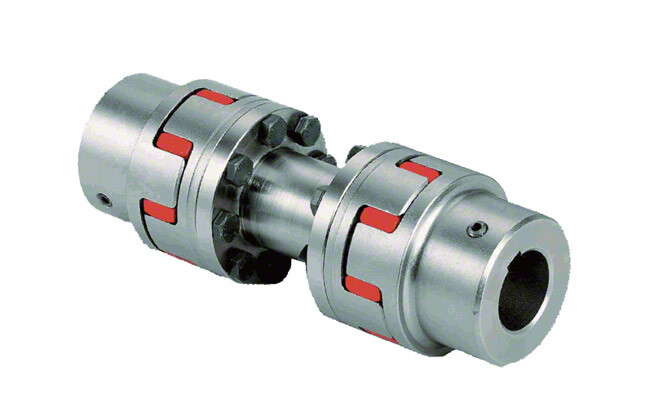

Comparison of Encoder Couplings with Other Coupling Types
When comparing encoder couplings with other coupling types, such as flexible couplings and magnetic couplings, several key factors come into play:
1. Flexibility: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, offer flexibility to accommodate misalignment between the encoder and the driven component. They provide angular, radial, and axial flexibility, ensuring efficient signal transmission while minimizing stress on components.
2. Signal Transmission: Encoder couplings are specifically designed to ensure accurate signal transmission between the encoder and the controlled system. This distinguishes them from other couplings that prioritize torque transmission, such as magnetic couplings used for sealing applications.
3. Backlash Reduction: Encoder couplings often prioritize low backlash to enhance the precision and accuracy of motion control systems. While some other coupling types also aim to minimize backlash, encoder couplings excel in this aspect due to their primary function of accurate signal transmission.
4. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings are commonly used for torque transmission across a sealed barrier, such as in pump applications. While they offer the advantage of hermetic sealing, they may not be as suitable for precise signal transmission as encoder couplings. Magnetic couplings can also introduce a certain amount of backlash due to their design.
5. Torque Capacity: Flexible couplings and some other types of couplings are often selected based on their torque capacity to transmit power between shafts. Encoder couplings, on the other hand, prioritize signal integrity and precision, making them ideal for applications where accurate motion control is essential.
6. Application Focus: Encoder couplings are specialized for motion control and automation systems that require precise positioning and accurate signal feedback. Other coupling types may have broader applications, including torque transmission, vibration dampening, and sealing.
7. Maintenance: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and accuracy. Magnetic couplings may have different maintenance requirements due to their sealing properties.
Overall, encoder couplings stand out in their ability to facilitate accurate signal transmission and precise motion control. While other coupling types have their own advantages and applications, encoder couplings are specifically tailored to meet the demands of motion control and automation systems where maintaining signal accuracy is paramount.

Proper Installation and Maintenance of Encoder Couplings
Proper installation and maintenance are essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of encoder couplings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Installation:
- Ensure Proper Alignment: Align the encoder coupling and shafts precisely to minimize misalignment, which can lead to signal loss and premature wear.
- Secure Fasteners: Tighten fasteners according to manufacturer specifications to prevent coupling slippage and maintain signal accuracy.
- Check Clearances: Ensure there’s enough clearance between the encoder coupling and surrounding components to prevent interference during operation.
- Use Proper Tools: Use appropriate tools and techniques during installation to avoid damaging the encoder coupling or other components.
2. Initial Testing:
- Perform System Check: After installation, conduct initial tests to verify proper signal transmission and alignment. Address any issues promptly.
- Check Signal Integrity: Use appropriate testing equipment to verify that the encoder signals are accurate and consistent.
3. Regular Maintenance:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the encoder coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Look for cracks, corrosion, or other irregularities.
- Lubrication: If the encoder coupling requires lubrication, follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure proper lubricant application and prevent excessive wear.
- Cleanliness: Keep the encoder coupling and its surroundings clean to prevent debris and contaminants from affecting performance.
- Monitor Temperature: Monitor operating temperatures to ensure the encoder coupling remains within its recommended temperature range.
4. Preventive Measures:
- Regular Checkups: Schedule periodic maintenance and inspections to catch potential issues before they lead to significant problems.
- Alignment Checks: Regularly verify shaft alignment to maintain accurate signal transmission and prevent premature wear.
- Replace as Needed: If the encoder coupling shows signs of significant wear, damage, or signal degradation, consider replacing it to avoid system failures.
5. Follow Manufacturer Recommendations:
- Adhere to the manufacturer’s installation, maintenance, and lubrication guidelines to ensure optimal performance and maintain warranty coverage.
By following these installation and maintenance practices, you can ensure that your encoder coupling functions reliably and efficiently, contributing to the overall performance of your motion control or automation system.

Choosing an Encoder Coupling: Key Considerations
When selecting an encoder coupling for a particular motion control or automation setup, several factors should be carefully considered:
1. Type of Misalignment: Identify the types of misalignment your system may encounter, such as angular, axial, or radial misalignment. Choose an encoder coupling that can effectively compensate for the specific misalignment your application might experience.
2. Torque and Load: Calculate the maximum torque and load that the coupling will need to transmit. Ensure that the selected coupling is rated to handle these loads without compromising performance or accuracy.
3. Backlash: Evaluate the allowable backlash based on the precision required for your application. Choose a coupling with minimal backlash to ensure accurate signal transmission.
4. Response Time: For applications requiring rapid changes in position or speed, select an encoder coupling with a low torsional stiffness. This enhances the response time of the system and ensures timely signal transmission.
5. Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment, including factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Choose a coupling material that can withstand the environmental conditions without degradation.
6. Shaft Size and Diameter: Ensure that the coupling is compatible with the shaft size and diameter of both the encoder and the driven component. Proper sizing prevents slippage and ensures efficient signal transmission.
7. Radial and Axial Runout: Evaluate the allowable radial and axial runout to prevent unnecessary stress on the coupling and encoder. Choosing a coupling that accommodates these factors contributes to a longer service life.
8. Space Limitations: If your setup has limited space, choose a compact and lightweight encoder coupling that can fit within the available dimensions without hindering other components.
9. Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the coupling material with both the encoder and the driven component. This is particularly important if the coupling will be exposed to chemicals or other substances.
10. Installation and Maintenance: Select a coupling that is easy to install and maintain. This helps reduce downtime during installation and ensures the longevity of the coupling.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the most suitable encoder coupling for your specific motion control or automation application, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy.


editor by CX 2024-05-17
China Best Sales Flexible 19-32 Woodon China Encoder Couplings Universal Coupling SWC-I120b-295, SWC-I100dh-304+30, SWC-I120b-295
Product Description
| Product Name | Cardan Shaft |
| Product Model | SWC-I75A-335+40 |
| Main Material | 35CrMo or 45# Steel |
| Nominal Torque | 500 N.M |
| Normal Length | 335 mm |
| Length Compensation | 40 mm |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Crucial Industries and Applications for Encoder Couplings
Encoder couplings play a vital role in various industries and applications that require precise motion control and accurate signal transmission. Some examples include:
1. CNC Machining: In computer numerical control (CNC) machining, encoder couplings ensure accurate positioning of machine axes, resulting in precise and intricate machining of complex parts.
2. Robotics: Robotic systems rely on encoder couplings to enable precise movement control of robotic arms, ensuring accurate positioning and manipulation of objects in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare.
3. Semiconductor Manufacturing: In the semiconductor industry, encoder couplings are crucial for aligning and controlling the movement of wafer handling systems, which are essential for producing microchips and electronic components.
4. Printing and Packaging: In printing and packaging machinery, encoder couplings ensure precise control of printing heads, paper feeding, and packaging processes, resulting in high-quality and consistent output.
5. Medical Equipment: Encoder couplings are used in medical equipment such as imaging devices, robotic surgery systems, and diagnostic equipment to enable accurate and controlled movement for medical procedures.
6. Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace applications, encoder couplings are employed in aircraft control systems, radar systems, and satellite positioning systems, ensuring precise navigation and communication.
7. Automated Assembly Lines: Industries using automated assembly lines, such as automotive manufacturing, rely on encoder couplings to synchronize the movement of conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other components.
8. Laboratory Automation: In laboratory settings, encoder couplings contribute to the precise movement of instruments and devices for sample handling, analysis, and testing.
These examples illustrate the wide range of industries and applications where encoder couplings are crucial for achieving accurate motion control and maintaining signal integrity.

Impact of Encoder Resolution on Choice of Coupling
The encoder resolution plays a crucial role in selecting an appropriate coupling for your system. Encoder resolution refers to the number of distinct positions a rotary encoder can detect in one full rotation. Here’s how encoder resolution impacts the choice of coupling:
1. Precision Requirements:
Higher encoder resolutions provide finer position accuracy. If your application demands high precision and accuracy, such as in robotics or CNC machines, a coupling that minimizes backlash and offers precise torque transmission is essential.
2. Backlash Sensitivity:
As encoder resolution increases, the system becomes more sensitive to backlash (play between coupling components). To mitigate this, a coupling with minimal backlash, such as a zero-backlash or low-backlash coupling, is recommended to ensure accurate position feedback.
3. Dynamic Response:
Higher encoder resolutions allow systems to detect even small movements, improving dynamic response. For applications requiring rapid and accurate positioning changes, a coupling that provides high torsional stiffness and low wind-up is beneficial.
4. Mechanical Compliance:
Low-resolution encoders may tolerate some misalignment due to their coarser feedback intervals. However, high-resolution encoders are more sensitive to misalignment, making it important to choose a coupling that accommodates misalignment while maintaining signal accuracy.
5. Coupling Selection:
For high-resolution encoders, consider couplings that provide precision, low backlash, and accurate torque transmission, such as beam couplings, bellows couplings, or Oldham couplings. These couplings help maintain the integrity of position feedback and optimize system performance.
6. Environmental Factors:
The operating environment can affect the choice of coupling. For applications with extreme conditions, such as temperature fluctuations or aggressive chemicals, select a coupling material that can withstand these conditions without compromising the encoder’s accuracy.
Ultimately, the encoder resolution influences the coupling choice by demanding a coupling that complements the precision, accuracy, and dynamic performance required by the application.

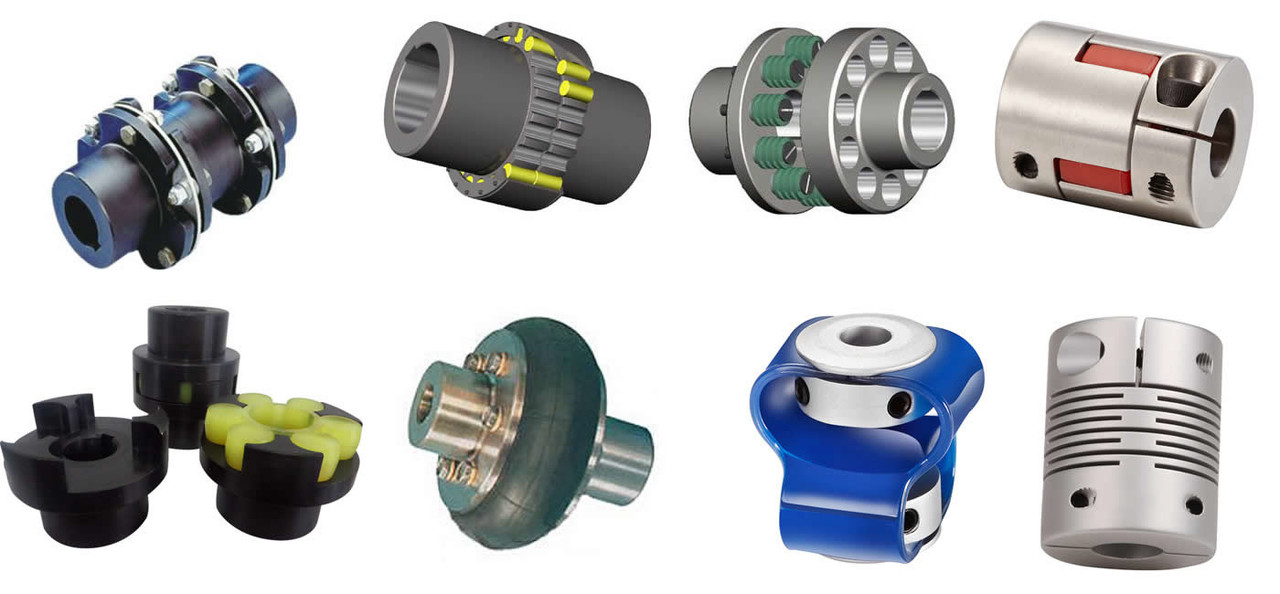
Types of Encoder Couplings Tailored for Specific Applications
Encoder couplings come in various types, each tailored to suit specific applications and requirements:
1. Beam Couplings: These couplings use flexible beams to transmit motion and accommodate misalignments. They are ideal for applications requiring high precision and low backlash.
2. Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings have accordion-like bellows that provide high torsional stiffness while allowing axial and angular misalignment compensation. They are commonly used in vacuum environments.
3. Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use a three-piece design to transmit motion. They provide high misalignment capacity while maintaining accurate motion transmission.
4. Disc Couplings: Disc couplings consist of thin metal discs that provide torsional stiffness and minimal backlash. They are suitable for high-speed and high-torque applications.
5. Flexible Shaft Couplings: These couplings use a flexible element, such as elastomer or rubber, to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations. They are versatile and used in various industries.
6. Miniature Couplings: Designed for small-scale applications, miniature couplings provide precise motion control in compact spaces, such as robotics and medical devices.
7. High-Torque Couplings: These couplings are built to handle high torque loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
8. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings use magnets to transmit motion without physical contact. They are used in applications requiring hermetic sealing or where avoiding direct contact is necessary.
9. Encoder-Integrated Couplings: Some couplings come with built-in encoders for direct position sensing. These are convenient for applications where space is limited or where separate encoders are not practical.
10. Shaft Locking Mechanisms: Some couplings feature mechanisms that lock the shafts in place, providing additional security against shaft slippage.
The choice of encoder coupling type depends on factors like the level of misalignment, torque requirements, speed, space limitations, and specific application needs.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China manufacturer Stainless Steel Aluminum Miniature Flexible Beam Coupling Encoder Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
A beam coupling, also known as helical coupling, is a flexible coupling for transmitting torque between 2 shafts while allowing for angular misalignment, parallel offset and even axial motion, of 1 shaft relative to the other. This design utilizes A single piece of material and becomes flexible by removal of material along a spiral path resulting in a curved flexible beam of helical shape. Since it is made from a single piece of material, the Beam Style coupling does not exhibit the backlash found in some multi-piece couplings. Another advantage of being an all machined coupling is the possibility to incorporate features into the final product while still keep the single piece integrity.
Changes to the lead of the helical beam provide changes to misalignment capabilities as well as other performance characteristics such as torque capacity and torsional stiffness. It is even possible to have multiple starts within the same helix.
The material used to manufacture the beam coupling also affects its performance and suitability for specific applications such as food, medical and aerospace. Materials are typically aluminum alloy and stainless steel, but they can also be made in acetal, maraging steel and titanium. The most common applications are attaching encoders to shafts and motion control for robotics.
Features
1.Materail: Aluminium alloy or steel
2.Elastic Spider: Three type of Elatic Spider can be choosed 86SH. A 92SH. A 98SH. A
3.Surface treatment: black finished / Anodizing
4.High sensitivity High torque rigid Zero back lash
5.Type of shaft lock: Set screw or Clamp type
6.Stock to ensure a prompt delivery with in 2 weeks.
7.High-performance with competitive prices.
Except our standard parts, we also can make the parts according customers’ drawing or design according customer requirement, please send us enquiry if there any need.
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
Packaging & Shipping
| Package | Standard suitable package / Pallet or container. Polybag inside export carton outside, blister and Tape and reel package available. If customers have specific requirements for the packaging, we will gladly accommodate. |
| Shipping |
10-20working days ofter payment receipt comfirmed (based on actual quantity). Professional goods shipping forward. |
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer?
A: We are factory.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment=1000USD, 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
We warmly welcome friends from domestic and abroad come to us for business negotiation and cooperation for mutual benefit. To supply customers excellent quality products with good price and punctual delivery time is our responsibility.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Crucial Industries and Applications for Encoder Couplings
Encoder couplings play a vital role in various industries and applications that require precise motion control and accurate signal transmission. Some examples include:
1. CNC Machining: In computer numerical control (CNC) machining, encoder couplings ensure accurate positioning of machine axes, resulting in precise and intricate machining of complex parts.
2. Robotics: Robotic systems rely on encoder couplings to enable precise movement control of robotic arms, ensuring accurate positioning and manipulation of objects in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare.
3. Semiconductor Manufacturing: In the semiconductor industry, encoder couplings are crucial for aligning and controlling the movement of wafer handling systems, which are essential for producing microchips and electronic components.
4. Printing and Packaging: In printing and packaging machinery, encoder couplings ensure precise control of printing heads, paper feeding, and packaging processes, resulting in high-quality and consistent output.
5. Medical Equipment: Encoder couplings are used in medical equipment such as imaging devices, robotic surgery systems, and diagnostic equipment to enable accurate and controlled movement for medical procedures.
6. Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace applications, encoder couplings are employed in aircraft control systems, radar systems, and satellite positioning systems, ensuring precise navigation and communication.
7. Automated Assembly Lines: Industries using automated assembly lines, such as automotive manufacturing, rely on encoder couplings to synchronize the movement of conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other components.
8. Laboratory Automation: In laboratory settings, encoder couplings contribute to the precise movement of instruments and devices for sample handling, analysis, and testing.
These examples illustrate the wide range of industries and applications where encoder couplings are crucial for achieving accurate motion control and maintaining signal integrity.

Best Practices for Minimizing Electrical Interference in Encoder Coupling Systems
Electrical interference can adversely affect the performance and accuracy of encoder coupling systems. To minimize such interference and ensure reliable signal transmission, consider the following best practices:
- Proper Grounding: Ensure that all components in the system are properly grounded to a common ground point. Grounding helps mitigate the buildup of static charges and reduces the risk of electrical noise affecting the encoder signal.
- Shielding: Use shielded cables for connecting the encoder to the controller. Shielding helps prevent external electromagnetic interference from reaching the signal wires and affecting the encoder output.
- Separation from Power Lines: Keep encoder cables and signal wires physically separated from high-voltage power lines, motors, and other sources of electromagnetic interference. This reduces the likelihood of induced noise affecting the encoder signal.
- Ferrite Beads: Employ ferrite beads or chokes on the signal cables near the encoder connection points. Ferrite beads suppress high-frequency noise and can be effective in minimizing electrical interference.
- Ground Loops: Avoid ground loops, which occur when there are multiple paths for current to flow between different ground points. Ground loops can introduce unwanted noise. Use single-point grounding and minimize ground loop formation.
- Isolation: Employ isolation techniques, such as optical isolation or transformer-based signal conditioning, to electrically isolate the encoder from the rest of the system. This prevents the propagation of noise between components.
- EMI Filters: Install electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters on the power supply lines to reduce conducted interference from reaching the encoder. These filters can help maintain clean power and reduce noise.
- Proper Cable Routing: Ensure that encoder cables are routed away from sources of interference and are kept as short as possible. Avoid sharp bends and kinks in the cables, which can lead to signal degradation.
- Grounding Practices: Follow proper grounding practices, such as using star grounding and minimizing ground connections. Avoid daisy-chaining ground connections, as this can increase the risk of interference.
Implementing these best practices will help minimize electrical interference and ensure that the encoder coupling system maintains accurate signal transmission, resulting in improved performance and reliability.

Choosing an Encoder Coupling: Key Considerations
When selecting an encoder coupling for a particular motion control or automation setup, several factors should be carefully considered:
1. Type of Misalignment: Identify the types of misalignment your system may encounter, such as angular, axial, or radial misalignment. Choose an encoder coupling that can effectively compensate for the specific misalignment your application might experience.
2. Torque and Load: Calculate the maximum torque and load that the coupling will need to transmit. Ensure that the selected coupling is rated to handle these loads without compromising performance or accuracy.
3. Backlash: Evaluate the allowable backlash based on the precision required for your application. Choose a coupling with minimal backlash to ensure accurate signal transmission.
4. Response Time: For applications requiring rapid changes in position or speed, select an encoder coupling with a low torsional stiffness. This enhances the response time of the system and ensures timely signal transmission.
5. Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment, including factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Choose a coupling material that can withstand the environmental conditions without degradation.
6. Shaft Size and Diameter: Ensure that the coupling is compatible with the shaft size and diameter of both the encoder and the driven component. Proper sizing prevents slippage and ensures efficient signal transmission.
7. Radial and Axial Runout: Evaluate the allowable radial and axial runout to prevent unnecessary stress on the coupling and encoder. Choosing a coupling that accommodates these factors contributes to a longer service life.
8. Space Limitations: If your setup has limited space, choose a compact and lightweight encoder coupling that can fit within the available dimensions without hindering other components.
9. Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the coupling material with both the encoder and the driven component. This is particularly important if the coupling will be exposed to chemicals or other substances.
10. Installation and Maintenance: Select a coupling that is easy to install and maintain. This helps reduce downtime during installation and ensures the longevity of the coupling.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the most suitable encoder coupling for your specific motion control or automation application, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China factory Gd Encoder Spring Coupling Rigid Coupling
Product Description
GD Encoder Spring Coupling Rigid Coupling
Description of GD Encoder Spring Coupling Rigid Coupling
>The main body is made of zinc alloy
>The middle elastomer is made of spring steel
>It has the advantages of simple structure, good flexibility, low inertia and less allowable angular deviation
>Easy installation, spring steel more effective compensation radial, shaft deviation
>Suitable for micro motor and encoder
>Fastening method of set screw
Catalogue of GD Encoder Spring Coupling Rigid Coupling
|
model parameter |
common bore diameter d1,d2 |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
F |
M |
tightening screw torque |
|
GD-16 x27 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,10 |
16 |
27 |
8.5 |
3 |
M3 |
0.7 |
|
GD-16 x35 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,10 |
16 |
35 |
12.5 |
3.5 |
M4 |
1.7 |
|
GD-26 x50 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,10,11,12,12.7,14 |
26 |
50 |
17 |
4.5 |
M5 |
4 |
|
model parameter |
Rated torque(N.m) |
Maximum torque(N.M) |
maximum speed (rpm) |
moment of inertia(Kg.M2) |
allowable eccentricity(mm) |
allowable deflection angle(°) |
weight (g) |
|
GD-16 x27 |
0.5 |
1 |
3000 |
1.02×10-6 |
1 |
8 |
30 |
|
GD-16 x35 |
0.5 |
1 |
3000 |
1.02×10-6 |
1 |
8 |
70 |
|
GD-26 x50 |
1.5 |
3 |
3000 |
1.15×10-5 |
1.2 |
8 |
130 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

High-Speed Rotations and Signal Accuracy in Encoder Couplings
Encoder couplings are designed to handle high-speed rotations while maintaining accurate signal transmission between the encoder and the driven shaft. Several factors contribute to their ability to achieve this:
1. Precision Manufacturing: Encoder couplings are manufactured with high precision to ensure minimal runout and concentricity errors. This precision minimizes vibrations and ensures accurate signal transmission at high speeds.
2. Low Backlash: Many encoder couplings are designed to have minimal or zero backlash. Backlash refers to the play or movement between the coupling’s mating components. Low backlash reduces signal inaccuracies caused by sudden changes in direction or speed.
3. Balanced Design: Balanced design helps distribute forces and torques evenly across the coupling, reducing the likelihood of vibration-induced signal distortions during high-speed rotations.
4. Material Selection: The choice of materials with suitable mechanical properties plays a role in achieving high-speed performance. Materials with low density and high strength help minimize the coupling’s mass while maintaining structural integrity.
5. Vibration Damping: Some encoder couplings incorporate vibration-damping features, such as elastomeric inserts, to mitigate vibrations and oscillations generated during high-speed rotations.
6. Dynamic Balance: Encoder couplings may undergo dynamic balancing to ensure that any uneven mass distribution is corrected, further reducing vibrations at high speeds.
7. Bearing Support: Proper bearing support on both sides of the encoder coupling helps maintain alignment and reduces stress on the coupling and encoder shaft, enhancing signal accuracy.
Encoder couplings are engineered to offer high-speed capabilities while preserving signal accuracy, making them suitable for applications where precision motion control and signal integrity are critical.

Best Practices for Minimizing Electrical Interference in Encoder Coupling Systems
Electrical interference can adversely affect the performance and accuracy of encoder coupling systems. To minimize such interference and ensure reliable signal transmission, consider the following best practices:
- Proper Grounding: Ensure that all components in the system are properly grounded to a common ground point. Grounding helps mitigate the buildup of static charges and reduces the risk of electrical noise affecting the encoder signal.
- Shielding: Use shielded cables for connecting the encoder to the controller. Shielding helps prevent external electromagnetic interference from reaching the signal wires and affecting the encoder output.
- Separation from Power Lines: Keep encoder cables and signal wires physically separated from high-voltage power lines, motors, and other sources of electromagnetic interference. This reduces the likelihood of induced noise affecting the encoder signal.
- Ferrite Beads: Employ ferrite beads or chokes on the signal cables near the encoder connection points. Ferrite beads suppress high-frequency noise and can be effective in minimizing electrical interference.
- Ground Loops: Avoid ground loops, which occur when there are multiple paths for current to flow between different ground points. Ground loops can introduce unwanted noise. Use single-point grounding and minimize ground loop formation.
- Isolation: Employ isolation techniques, such as optical isolation or transformer-based signal conditioning, to electrically isolate the encoder from the rest of the system. This prevents the propagation of noise between components.
- EMI Filters: Install electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters on the power supply lines to reduce conducted interference from reaching the encoder. These filters can help maintain clean power and reduce noise.
- Proper Cable Routing: Ensure that encoder cables are routed away from sources of interference and are kept as short as possible. Avoid sharp bends and kinks in the cables, which can lead to signal degradation.
- Grounding Practices: Follow proper grounding practices, such as using star grounding and minimizing ground connections. Avoid daisy-chaining ground connections, as this can increase the risk of interference.
Implementing these best practices will help minimize electrical interference and ensure that the encoder coupling system maintains accurate signal transmission, resulting in improved performance and reliability.

Types of Encoder Couplings Tailored for Specific Applications
Encoder couplings come in various types, each tailored to suit specific applications and requirements:
1. Beam Couplings: These couplings use flexible beams to transmit motion and accommodate misalignments. They are ideal for applications requiring high precision and low backlash.
2. Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings have accordion-like bellows that provide high torsional stiffness while allowing axial and angular misalignment compensation. They are commonly used in vacuum environments.
3. Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use a three-piece design to transmit motion. They provide high misalignment capacity while maintaining accurate motion transmission.
4. Disc Couplings: Disc couplings consist of thin metal discs that provide torsional stiffness and minimal backlash. They are suitable for high-speed and high-torque applications.
5. Flexible Shaft Couplings: These couplings use a flexible element, such as elastomer or rubber, to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations. They are versatile and used in various industries.
6. Miniature Couplings: Designed for small-scale applications, miniature couplings provide precise motion control in compact spaces, such as robotics and medical devices.
7. High-Torque Couplings: These couplings are built to handle high torque loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
8. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings use magnets to transmit motion without physical contact. They are used in applications requiring hermetic sealing or where avoiding direct contact is necessary.
9. Encoder-Integrated Couplings: Some couplings come with built-in encoders for direct position sensing. These are convenient for applications where space is limited or where separate encoders are not practical.
10. Shaft Locking Mechanisms: Some couplings feature mechanisms that lock the shafts in place, providing additional security against shaft slippage.
The choice of encoder coupling type depends on factors like the level of misalignment, torque requirements, speed, space limitations, and specific application needs.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China factory OEM Aluminum Stainless Steel Motor Jaw Encoder Shaft Coupling
Product Description
JMII Type Diaphragm Coupling(JB/T9147-1999)
JMII Elastic Diaphragm Coupling belong to JM series diaphragm couplings. They are made up of several groups of diaphragms (stainless steel thin wrench), and bolts are interlaced with 2 halves of couplings. Each diaphragm is made up of several sheets. The diaphragm is divided into connecting rod type and whole shape with different shapes. Its elastic deformation is used to compensate the relative displacement of the 2 axes, and it is a high performance flexible coupling of metal elastic elements. No lubrication, compact structure, high strength, long service life, no rotation clearance, no influence on temperature and oil pollution, it has the characteristics of acid resistance, alkali resistance and corrosion resistance.
JMII Type Diaphragm Coupling Main Dimension(JB/T9147-1999)
| Type | Nominal torque Tn |
Peak torque Tmax |
Max Speed nmax |
Bore Diameter d,d1 |
Bore length | D | D1 | t | Torsional rigidity×106 | Mass | Rotary inertia |
||
| J1 type | Y type |
L (recommend) |
|||||||||||
| L | |||||||||||||
| N·m | N·m | r·min-1 | mm | N·m/rad | kg | kg·m2 | |||||||
| JMII1 | 40 | 63 | 10700 | 14 | 27 | 32 | 35 | 80 | 39 | 8±0.2 | 0.37 | 0.9 | 0.0005 |
| 16,18,19 | 30 | 42 | |||||||||||
| 20,22,24 | 38 | 52 | |||||||||||
| 25,28 | 44 | 62 | |||||||||||
| JMII2 | 63 | 100 | 9300 | 20,22,24 | 38 | 52 | 40 | 92 | 53 | 0.45 | 1.4 | 0.0011 | |
| 25,28 | 44 | 62 | |||||||||||
| 30,32,35,38 | 60 | 82 | |||||||||||
| JMII3 | 100 | 200 | 8400 | 25,28 | 44 | 62 | 45 | 102 | 63 | 0.56 | 2.1 | 0.002 | |
| 30,32,35,38 | 60 | 82 | |||||||||||
| 40,42,45 | 84 | 112 | |||||||||||
| JMII4 | 250 | 400 | 6700 | 30,32,35,38 | 60 | 82 | 55 | 128 | 77 | 11±0.3 | 0.81 | 4.2 | 0.006 |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55 | 84 | 112 | |||||||||||
| JMII5 | 500 | 800 | 5900 | 35,38 | 60 | 82 | 65 | 145 | 91 | 1.2 | 6.4 | 0.012 | |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | |||||||||||
| 60,63,65 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| JMII6 | 800 | 1250 | 5100 | 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | 75 | 168 | 105 | 14±0.3 | 1.42 | 9.6 | 0.571 |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| JMII7 | 1000 | 2000 | 4750 | 45,48,50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | 80 | 180 | 112 | 15±0.4 | 1.9 | 12.5 | 0.0365 |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII8 | 1600 | 3150 | 4300 | 50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | 200 | 120 | 2.35 | 15.5 | 0.057 | ||
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80,85 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII9 | 2500 | 4000 | 4200 | 55,56 | 84 | 112 | 205 | 120 | 20±0.4 | 2.7 | 16.5 | 0.065 | |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80,85 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII10 | 3150 | 5000 | 4000 | 55,56 | 84 | 112 | 90 | 215 | 128 | 20±0.4 | 3.02 | 19.5 | 0.083 |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80,85,90 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII11 | 4000 | 6300 | 3650 | 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 100 | 235 | 132 | 23±0.5 | 3.46 | 25 | 0.131 |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII12 | 5000 | 8000 | 3400 | 63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 250 | 145 | 3.67 | 30 | 0.174 | ||
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII13 | 6300 | 10000 | 3200 | 63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 110 | 270 | 155 | 5.2 | 36 | 0.239 | |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII14 | 8000 | 12500 | 2850 | 65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 115 | 300 | 162 | 27±0.6 | 7.8 | 45 | 0.38 |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII15 | 10000 | 16000 | 2700 | 70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 125 | 320 | 176 | 8.43 | 55 | 0.5 | |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII16 | 12500 | 20000 | 2450 | 75 | 107 | 142 | 140 | 350 | 186 | 32±0.7 | 10.23 | 75 | 0.85 |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| 130 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| JMII17 | 16000 | 25000 | 2300 | 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | 145 | 370 | 203 | 10.97 | 85 | 1.1 | |
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| 130,140 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| JMII18 | 20000 | 31500 | 2150 | 90,95 | 132 | 172 | 165 | 400 | 230 | 13.07 | 115 | 1.65 | |
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| JMII19 | 25000 | 40000 | 1950 | 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | 175 | 440 | 245 | 38±0.9 | 14.26 | 150 | 2.69 |
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160,170 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| JMII20 | 31500 | 50000 | 1850 | 110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | 185 | 460 | 260 | 22.13 | 170 | 3.28 | |
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| JMII21 | 35500 | 56000 | 1800 | 120,125 | 167 | 212 | 200 | 480 | 280 | 38±0.9 | 23.7 | 200 | 4.28 |
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| JMII22 | 40000 | 63000 | 1700 | 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | 210 | 500 | 295 | 24.6 | 230 | 5.18 | |
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| JMII23 | 50000 | 80000 | 1600 | 140,150 | 202 | 252 | 220 | 540 | 310 | 44±1 | 29.71 | 275 | 7.7 |
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| JMII24 | 63000 | 10000 | 1450 | 150 | 202 | 252 | 240 | 600 | 335 | 50±1.2 | 32.64 | 380 | 9.3 |
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| 240 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| JMII25 | 80000 | 125000 | 1400 | 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | 255 | 620 | 350 | 37.69 | 410 | 15.3 | |
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| 240,250 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| JMII26 | 90000 | 140000 | 1300 | 160 | 242 | 302 | 275 | 660 | 385 | 50.43 | 510 | 20.9 | |
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| JMII27 | 112000 | 180000 | 1200 | 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | 295 | 720 | 410 | 60±1.4 | 71.51 | 620 | 32.4 |
| 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| 280 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| JMII28 | 140000 | 20000 | 1150 | 220 | 282 | 352 | 300 | 740 | 420 | 93.37 | 680 | 36 | |
| 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| 280,300 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| JMII29 | 160000 | 224000 | 1100 | 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | 320 | 770 | 450 | 114.53 | 780 | 43.9 | |
| 280,300,320 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| JMII30 | 180000 | 280000 | 1050 | 250,260 | 330 | 410 | 350 | 820 | 490 | 130.76 | 950 | 60.5 | |
| 280,300,320 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| 340 | 450 | 550 | |||||||||||
Product Display
♦Other Products List
| Transmission Machinery Parts Name |
Model |
| Universal Coupling | WS,WSD,WSP |
| Cardan Shaft | SWC,SWP,SWZ |
| Tooth Coupling | CL,CLZ,GCLD,GIICL, GICL,NGCL,GGCL,GCLK |
| Disc Coupling | JMI,JMIJ,JMII,JMIIJ |
| High Flexible Coupling | LM |
| Chain Coupling | GL |
| Jaw Coupling | LT |
| Grid Coupling | JS |
♦Our Company
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the design and manufacture of various types of coupling. There are 86 employees in our company, including 2 senior engineers and no fewer than 20 mechanical design and manufacture, heat treatment, welding, and other professionals.
Advanced and reasonable process, complete detection means. Our company actively introduces foreign advanced technology and equipment, on the basis of the condition, we make full use of the advantage and do more research and innovation. Strict to high quality and operate strictly in accordance with the ISO9000 quality certification system standard mode.
Our company supplies different kinds of products. High quality and reasonable price. We stick to the principle of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement and innovation to meet the customers” for the management and “zero defect, zero complaints” as the quality objective.
♦Our Services
1. Design Services
Our design team has experience in Cardan shafts relating to product design and development. If you have any needs for your new product or wish to make further improvements, we are here to offer our support.
2. Product Services
raw materials → Cutting → Forging →Rough machining →Shot blasting →Heat treatment →Testing →Fashioning →Cleaning→ Assembly→Packing→Shipping
3. Samples Procedure
We could develop the sample according to your requirement and amend the sample constantly to meet your need.
4. Research & Development
We usually research the new needs of the market and develop new models when there are new cars in the market.
5. Quality Control
Every step should be a particular test by Professional Staff according to the standard of ISO9001 and TS16949.
♦FAQ
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing
various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all customers with customized PDF or AI format artworks.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: Do you provide samples? Is it free or extra?
Yes, we could offer the sample but not for free. Actually, we have an excellent price principle, when you make the bulk order the cost of the sample will be deducted.
Q 5: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 6: What is the MOQ?
A: Usually our MOQ is 1pcs.
Q 7: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 8: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
Q 9: What’s your payment?
A:1) T/T.
♦Contact Us
Web: huadingcoupling
Add: No.11 HangZhou Road,Chengnan park,HangZhou City,ZheJiang Province,China /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Industry Standards and Guidelines for Selecting and Installing Encoder Couplings
While there are no specific industry standards exclusively focused on encoder couplings, various general standards and guidelines related to couplings and motion control systems can be applied. These standards ensure proper selection, installation, and operation of encoder couplings:
1. ISO Standards: ISO (International Organization for Standardization) has developed standards related to couplings, such as ISO 14691 for flexible couplings and ISO 15364 for gear couplings. Although not specific to encoder couplings, these standards provide guidance on aspects like dimensions, tolerances, and testing methods.
2. Manufacturer Recommendations: Encoder coupling manufacturers often provide guidelines for selecting and installing their products. These guidelines include information on torque ratings, misalignment capabilities, and installation procedures specific to their coupling designs.
3. Motion Control Associations: Organizations such as the Motion Control & Motor Association (MCMA) provide resources and best practices for selecting and integrating motion control components, including encoder couplings. They offer insights into achieving optimal performance, accuracy, and reliability.
4. Machinery Safety Standards: Depending on the application, machinery safety standards such as ISO 13849 or ANSI B11.19 may need to be considered. These standards ensure the safe integration of motion control systems and related components.
5. OEM and System Requirements: The original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or specific system requirements for the machinery or automation setup should also be considered when selecting and installing encoder couplings. These requirements may include environmental conditions, space limitations, and performance expectations.
When selecting and installing encoder couplings, it’s essential to follow the guidelines provided by the coupling manufacturer and consider relevant industry standards. Additionally, consulting with experts in the field of motion control and automation can help ensure that the chosen encoder coupling meets the specific needs of the application and complies with safety and performance standards.

Best Practices for Minimizing Electrical Interference in Encoder Coupling Systems
Electrical interference can adversely affect the performance and accuracy of encoder coupling systems. To minimize such interference and ensure reliable signal transmission, consider the following best practices:
- Proper Grounding: Ensure that all components in the system are properly grounded to a common ground point. Grounding helps mitigate the buildup of static charges and reduces the risk of electrical noise affecting the encoder signal.
- Shielding: Use shielded cables for connecting the encoder to the controller. Shielding helps prevent external electromagnetic interference from reaching the signal wires and affecting the encoder output.
- Separation from Power Lines: Keep encoder cables and signal wires physically separated from high-voltage power lines, motors, and other sources of electromagnetic interference. This reduces the likelihood of induced noise affecting the encoder signal.
- Ferrite Beads: Employ ferrite beads or chokes on the signal cables near the encoder connection points. Ferrite beads suppress high-frequency noise and can be effective in minimizing electrical interference.
- Ground Loops: Avoid ground loops, which occur when there are multiple paths for current to flow between different ground points. Ground loops can introduce unwanted noise. Use single-point grounding and minimize ground loop formation.
- Isolation: Employ isolation techniques, such as optical isolation or transformer-based signal conditioning, to electrically isolate the encoder from the rest of the system. This prevents the propagation of noise between components.
- EMI Filters: Install electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters on the power supply lines to reduce conducted interference from reaching the encoder. These filters can help maintain clean power and reduce noise.
- Proper Cable Routing: Ensure that encoder cables are routed away from sources of interference and are kept as short as possible. Avoid sharp bends and kinks in the cables, which can lead to signal degradation.
- Grounding Practices: Follow proper grounding practices, such as using star grounding and minimizing ground connections. Avoid daisy-chaining ground connections, as this can increase the risk of interference.
Implementing these best practices will help minimize electrical interference and ensure that the encoder coupling system maintains accurate signal transmission, resulting in improved performance and reliability.

Types of Encoder Couplings Tailored for Specific Applications
Encoder couplings come in various types, each tailored to suit specific applications and requirements:
1. Beam Couplings: These couplings use flexible beams to transmit motion and accommodate misalignments. They are ideal for applications requiring high precision and low backlash.
2. Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings have accordion-like bellows that provide high torsional stiffness while allowing axial and angular misalignment compensation. They are commonly used in vacuum environments.
3. Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use a three-piece design to transmit motion. They provide high misalignment capacity while maintaining accurate motion transmission.
4. Disc Couplings: Disc couplings consist of thin metal discs that provide torsional stiffness and minimal backlash. They are suitable for high-speed and high-torque applications.
5. Flexible Shaft Couplings: These couplings use a flexible element, such as elastomer or rubber, to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations. They are versatile and used in various industries.
6. Miniature Couplings: Designed for small-scale applications, miniature couplings provide precise motion control in compact spaces, such as robotics and medical devices.
7. High-Torque Couplings: These couplings are built to handle high torque loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
8. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings use magnets to transmit motion without physical contact. They are used in applications requiring hermetic sealing or where avoiding direct contact is necessary.
9. Encoder-Integrated Couplings: Some couplings come with built-in encoders for direct position sensing. These are convenient for applications where space is limited or where separate encoders are not practical.
10. Shaft Locking Mechanisms: Some couplings feature mechanisms that lock the shafts in place, providing additional security against shaft slippage.
The choice of encoder coupling type depends on factors like the level of misalignment, torque requirements, speed, space limitations, and specific application needs.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China wholesaler China DIY Plum Coupling and Flexible Couplings and Exhaust Flexible Coupling and FCL Flexible Encoder Shaft Coupling FCL560
Product Description
Product Description
FCL Coupling/Shaft Coupling /Pin & Bush Coupling /FCL Flexible Coupling/NBK FCL Coupling is widely used for its compacts designing, easy installation, convenient maintenance, small and light weight.
As long as the relative displacement between shafts is kept within the specified tolerance, couplings will operate the best function and have a longer working life.
Thus it is greatly demanded in medium and minor power transmission systems driven by motors, such as speed reducers, hoists, compressors, conveyors, spinning and weaving machines and ball mills.
Technical Date
| KASIN No. | A | d | L | C1 | C2 | B | F1 | F2 | n | a | M | t | PartsNo. | Max. Torque | Max.R.P.M | Eccentricity | Angularity | End-Play | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FCL 1/8822 0571 -57152031 Fax: 86~/8822 0571 -57152030 Http://kasinchain /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Comparison of Encoder Couplings with Other Coupling TypesWhen comparing encoder couplings with other coupling types, such as flexible couplings and magnetic couplings, several key factors come into play: 1. Flexibility: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, offer flexibility to accommodate misalignment between the encoder and the driven component. They provide angular, radial, and axial flexibility, ensuring efficient signal transmission while minimizing stress on components. 2. Signal Transmission: Encoder couplings are specifically designed to ensure accurate signal transmission between the encoder and the controlled system. This distinguishes them from other couplings that prioritize torque transmission, such as magnetic couplings used for sealing applications. 3. Backlash Reduction: Encoder couplings often prioritize low backlash to enhance the precision and accuracy of motion control systems. While some other coupling types also aim to minimize backlash, encoder couplings excel in this aspect due to their primary function of accurate signal transmission. 4. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings are commonly used for torque transmission across a sealed barrier, such as in pump applications. While they offer the advantage of hermetic sealing, they may not be as suitable for precise signal transmission as encoder couplings. Magnetic couplings can also introduce a certain amount of backlash due to their design. 5. Torque Capacity: Flexible couplings and some other types of couplings are often selected based on their torque capacity to transmit power between shafts. Encoder couplings, on the other hand, prioritize signal integrity and precision, making them ideal for applications where accurate motion control is essential. 6. Application Focus: Encoder couplings are specialized for motion control and automation systems that require precise positioning and accurate signal feedback. Other coupling types may have broader applications, including torque transmission, vibration dampening, and sealing. 7. Maintenance: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and accuracy. Magnetic couplings may have different maintenance requirements due to their sealing properties. Overall, encoder couplings stand out in their ability to facilitate accurate signal transmission and precise motion control. While other coupling types have their own advantages and applications, encoder couplings are specifically tailored to meet the demands of motion control and automation systems where maintaining signal accuracy is paramount.
Design Influence on Encoder Coupling’s Handling of Angular MisalignmentThe design of an encoder coupling plays a crucial role in its ability to handle angular misalignment between shafts. Here’s how the design factors influence this capability:
In summary, the design of an encoder coupling directly influences its capacity to handle angular misalignment, ensuring smooth signal transmission and accurate motion control.
Key Functions and Benefits of Using an Encoder CouplingAn encoder coupling plays a vital role in motion control and automation systems, offering several functions and benefits: 1. Accurate Position and Speed Sensing: Encoder couplings ensure precise transmission of rotational motion between the motor and the encoder, allowing accurate measurement of position and speed. 2. Misalignment Compensation: They can accommodate angular, radial, and axial misalignments between the motor and encoder shafts, maintaining accurate motion even in imperfect alignment conditions. 3. Torsional Stiffness: Encoder couplings provide torsional rigidity to minimize torsional deflection, ensuring that the encoder’s output signals accurately reflect the actual motion of the motor. 4. Signal Integrity: By maintaining precise alignment, they prevent signal distortion or loss, leading to accurate position and speed feedback from the encoder. 5. Reduced Wear: Proper alignment reduces stress on shafts, bearings, and other components, prolonging the lifespan of both the motor and encoder. 6. Increased Efficiency: Encoder couplings help achieve smoother motion control, enhancing overall system efficiency and reducing the likelihood of jerky movements. 7. Enhanced Performance: With accurate position and speed feedback, encoder couplings contribute to improved system performance, consistency, and repeatability. 8. Flexible Design: They come in various designs and materials to suit different applications and requirements. 9. Compatibility: Encoder couplings are compatible with various motor and encoder types, making them versatile solutions for different setups. 10. Easy Installation: Most encoder couplings are designed for straightforward installation, reducing downtime during setup or maintenance. Overall, encoder couplings are essential components that ensure precise motion control, accurate position sensing, and reliable automation in various industries and applications.
China Hot selling Helical Drive Flexible Coupling for Encoder Shaft CouplingProduct Description
Helical Drive Flexible Coupling For Encoder Shaft Coupling Dimensions Product Description Coupling refers to a device that connects 2 shafts or shafts and rotating parts, rotates together during the transmission of motion and power, and does not disengage under normal conditions. Sometimes it is also usedas a safety device to prevent the connected parts from bearing excessive load, which plays the role of overload protection.
Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings. Rigid couplings do not have buffering property and the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes. It is required that the 2 axes be strictly aligned. However, such couplings are simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost, convenient in assembly and disassembly, and maintenance, which can ensure that the 2 axes are relatively neutral, have large transmission torque, and are widely used. Commonly used are flange coupling, sleeve coupling and jacket coupling. Flexible coupling can also be divided into flexible coupling without elastic element and flexible coupling with elastic element. The former type only has the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes, but cannot cushion and reduce vibration. Common types include slider coupling, gear coupling, universal coupling and chain coupling; The latter type contains elastic elements. In addition to the ability to compensate the relative displacement Our leading mainly including universal couplings, drum gear couplings, elastic couplings etc.
Coupling performance
Inspection equipment: How to select the appropriate coupling type FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Comparison of Encoder Couplings with Other Coupling TypesWhen comparing encoder couplings with other coupling types, such as flexible couplings and magnetic couplings, several key factors come into play: 1. Flexibility: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, offer flexibility to accommodate misalignment between the encoder and the driven component. They provide angular, radial, and axial flexibility, ensuring efficient signal transmission while minimizing stress on components. 2. Signal Transmission: Encoder couplings are specifically designed to ensure accurate signal transmission between the encoder and the controlled system. This distinguishes them from other couplings that prioritize torque transmission, such as magnetic couplings used for sealing applications. 3. Backlash Reduction: Encoder couplings often prioritize low backlash to enhance the precision and accuracy of motion control systems. While some other coupling types also aim to minimize backlash, encoder couplings excel in this aspect due to their primary function of accurate signal transmission. 4. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings are commonly used for torque transmission across a sealed barrier, such as in pump applications. While they offer the advantage of hermetic sealing, they may not be as suitable for precise signal transmission as encoder couplings. Magnetic couplings can also introduce a certain amount of backlash due to their design. 5. Torque Capacity: Flexible couplings and some other types of couplings are often selected based on their torque capacity to transmit power between shafts. Encoder couplings, on the other hand, prioritize signal integrity and precision, making them ideal for applications where accurate motion control is essential. 6. Application Focus: Encoder couplings are specialized for motion control and automation systems that require precise positioning and accurate signal feedback. Other coupling types may have broader applications, including torque transmission, vibration dampening, and sealing. 7. Maintenance: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and accuracy. Magnetic couplings may have different maintenance requirements due to their sealing properties. Overall, encoder couplings stand out in their ability to facilitate accurate signal transmission and precise motion control. While other coupling types have their own advantages and applications, encoder couplings are specifically tailored to meet the demands of motion control and automation systems where maintaining signal accuracy is paramount.
Impact of Encoder Resolution on Choice of CouplingThe encoder resolution plays a crucial role in selecting an appropriate coupling for your system. Encoder resolution refers to the number of distinct positions a rotary encoder can detect in one full rotation. Here’s how encoder resolution impacts the choice of coupling: 1. Precision Requirements: Higher encoder resolutions provide finer position accuracy. If your application demands high precision and accuracy, such as in robotics or CNC machines, a coupling that minimizes backlash and offers precise torque transmission is essential. 2. Backlash Sensitivity: As encoder resolution increases, the system becomes more sensitive to backlash (play between coupling components). To mitigate this, a coupling with minimal backlash, such as a zero-backlash or low-backlash coupling, is recommended to ensure accurate position feedback. 3. Dynamic Response: Higher encoder resolutions allow systems to detect even small movements, improving dynamic response. For applications requiring rapid and accurate positioning changes, a coupling that provides high torsional stiffness and low wind-up is beneficial. 4. Mechanical Compliance: Low-resolution encoders may tolerate some misalignment due to their coarser feedback intervals. However, high-resolution encoders are more sensitive to misalignment, making it important to choose a coupling that accommodates misalignment while maintaining signal accuracy. 5. Coupling Selection: For high-resolution encoders, consider couplings that provide precision, low backlash, and accurate torque transmission, such as beam couplings, bellows couplings, or Oldham couplings. These couplings help maintain the integrity of position feedback and optimize system performance. 6. Environmental Factors: The operating environment can affect the choice of coupling. For applications with extreme conditions, such as temperature fluctuations or aggressive chemicals, select a coupling material that can withstand these conditions without compromising the encoder’s accuracy. Ultimately, the encoder resolution influences the coupling choice by demanding a coupling that complements the precision, accuracy, and dynamic performance required by the application.
Choosing an Encoder Coupling: Key ConsiderationsWhen selecting an encoder coupling for a particular motion control or automation setup, several factors should be carefully considered: 1. Type of Misalignment: Identify the types of misalignment your system may encounter, such as angular, axial, or radial misalignment. Choose an encoder coupling that can effectively compensate for the specific misalignment your application might experience. 2. Torque and Load: Calculate the maximum torque and load that the coupling will need to transmit. Ensure that the selected coupling is rated to handle these loads without compromising performance or accuracy. 3. Backlash: Evaluate the allowable backlash based on the precision required for your application. Choose a coupling with minimal backlash to ensure accurate signal transmission. 4. Response Time: For applications requiring rapid changes in position or speed, select an encoder coupling with a low torsional stiffness. This enhances the response time of the system and ensures timely signal transmission. 5. Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment, including factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Choose a coupling material that can withstand the environmental conditions without degradation. 6. Shaft Size and Diameter: Ensure that the coupling is compatible with the shaft size and diameter of both the encoder and the driven component. Proper sizing prevents slippage and ensures efficient signal transmission. 7. Radial and Axial Runout: Evaluate the allowable radial and axial runout to prevent unnecessary stress on the coupling and encoder. Choosing a coupling that accommodates these factors contributes to a longer service life. 8. Space Limitations: If your setup has limited space, choose a compact and lightweight encoder coupling that can fit within the available dimensions without hindering other components. 9. Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the coupling material with both the encoder and the driven component. This is particularly important if the coupling will be exposed to chemicals or other substances. 10. Installation and Maintenance: Select a coupling that is easy to install and maintain. This helps reduce downtime during installation and ensures the longevity of the coupling. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the most suitable encoder coupling for your specific motion control or automation application, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy.
China OEM CHINAMFG Customized Steel Flexible Spring Bellow Shaft Coupling Flexible Encoder CouplingProduct Description
Densen customized steel flexible spring bellow shaft coupling flexible encoder coupling
Product show Company Information HangZhou New CHINAMFG Casting and Forging Company is the sales company of HangZhou CHINAMFG Group of Companies. Features of New CHINAMFG simply summarized as below: 1. Trusted supplier of steel, iron & non-ferrous components; 2. Extensive documented quality program in place. 3. Castings, forgings, stampings, machining, welding & fabrication services. 4. 9 related factories, over 50 joint-venture sub-contractors. 5. 25+ years of manufacturing experiences, 10+ years of exporting experience 6. 100% of products sold to overseas customers. 7. 50% of customer base is forturne 500 companies.
Processing support Casting Service: Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. New Densen offers multiple investment casting, sand casting, permanent casting, die casting, low pressure casting, ESR casting, lost foam casting, etc. Material can be handled include steel, iron, non-ferrous. Single component weight range is from 0.01Kg to 150 tons separately.
Forging Service: Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. New CHINAMFG offers open die forging, closed die forging and ring forging services. Material can be steel, iron and non-ferrous. Material can be handled include steel, iron, non-ferrous. Single component weight range is from 0.1Kg to 50,000Kgs.
Stamping Service: Stamping (also known as punching) is the process of placing flat sheet metal in either blank or coil form into a stamping press where a tool and die surface forms the metal into a net shape. New Densen-XBL has more than 60 sets stamping equipments, is the designed supplier for several famous bands automotive companies, has the full ability to offer whole processes from blanking, stamping, welding, to electrostatic spraying for CHINAMFG customers.
Welding & Fabrication Service: Welding Frabrication is the fabrication process of metal structures by cutting, bending, then assembling the components together through welding New CHINAMFG offers manual arc welding ,laser welding and robot welding etc. UT, MPT,RT,PT all are available used for inspection, WPS &PQR (Welding Process Specification& Procedure Qualification Records) before production is available under clients’ requirement.
Machining Service: Machining is any of various processes in which a piece of raw material is cut into a desired final shape and size by a controlled material-removal process. New Densen-XBL has more than 60 sets precision machines incl. CNC center, boring, milling, lathing, etc., and more than 300 inspection instruments incl. 3 sets CMM with grade μm. Repeated tolerance can be maintained as 0.02mm. Meanwhile awarded by certificates ISO9001-2008; ISO/TS16949. New Densen-XBL specialized in high precise machining for small-middle-big metal components.
3rd Party Inspection:
New Densen worked as 3rd party inspection center besides its sister factories or sub-contractors’ self inspection, Offers process inspection, random inspection and before delivedry inspection services for material, mechanical, inside defects, dimentional, pressure, load, balance, surface treatment, visual inspection and test. Weekly project follow-up report together with pictures and videos, full quality inspection documentation available. New CHINAMFG also designed as 3rd party inspection representative for several customers when their products made by other suppliers.
Application:
Contact us /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
High-Speed Rotations and Signal Accuracy in Encoder CouplingsEncoder couplings are designed to handle high-speed rotations while maintaining accurate signal transmission between the encoder and the driven shaft. Several factors contribute to their ability to achieve this: 1. Precision Manufacturing: Encoder couplings are manufactured with high precision to ensure minimal runout and concentricity errors. This precision minimizes vibrations and ensures accurate signal transmission at high speeds. 2. Low Backlash: Many encoder couplings are designed to have minimal or zero backlash. Backlash refers to the play or movement between the coupling’s mating components. Low backlash reduces signal inaccuracies caused by sudden changes in direction or speed. 3. Balanced Design: Balanced design helps distribute forces and torques evenly across the coupling, reducing the likelihood of vibration-induced signal distortions during high-speed rotations. 4. Material Selection: The choice of materials with suitable mechanical properties plays a role in achieving high-speed performance. Materials with low density and high strength help minimize the coupling’s mass while maintaining structural integrity. 5. Vibration Damping: Some encoder couplings incorporate vibration-damping features, such as elastomeric inserts, to mitigate vibrations and oscillations generated during high-speed rotations. 6. Dynamic Balance: Encoder couplings may undergo dynamic balancing to ensure that any uneven mass distribution is corrected, further reducing vibrations at high speeds. 7. Bearing Support: Proper bearing support on both sides of the encoder coupling helps maintain alignment and reduces stress on the coupling and encoder shaft, enhancing signal accuracy. Encoder couplings are engineered to offer high-speed capabilities while preserving signal accuracy, making them suitable for applications where precision motion control and signal integrity are critical.
Recent Advancements in Encoder Coupling TechnologyRecent years have seen several advancements and innovations in encoder coupling technology, aimed at enhancing performance, accuracy, and reliability. Some notable developments include: 1. High-Resolution Encoders: Couplings integrated with high-resolution encoders offer finer position feedback, enabling precise motion control in applications requiring high accuracy. 2. Compact and Lightweight Designs: Innovations in materials and design have led to more compact and lightweight encoder couplings, suitable for space-constrained environments. 3. Zero-Backlash Designs: Advanced coupling designs have reduced or eliminated backlash, improving positioning accuracy and repeatability in motion control systems. 4. Multi-Functionality: Some encoder couplings now integrate additional functionalities, such as torque measurement, temperature sensing, or vibration monitoring, expanding their capabilities within a single component. 5. Non-Contact Couplings: Non-contact encoder couplings, utilizing magnetic or optical technologies, eliminate mechanical wear and offer maintenance-free operation while maintaining signal accuracy. 6. Enhanced Material Selection: The use of advanced materials with high fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability contributes to improved coupling durability and longevity. 7. Smart Couplings: Integration with smart technologies, such as IoT connectivity and real-time data monitoring, enables remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and system optimization. 8. Customization: Advances in manufacturing techniques allow for custom-designed encoder couplings tailored to specific applications, optimizing performance and reliability. 9. Environmental Resistance: Modern encoder couplings are engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, chemicals, and contaminants. 10. Industry-Specific Solutions: Innovations in encoder coupling technology cater to industry-specific needs, such as robotics, automation, aerospace, and medical equipment. These recent advancements in encoder coupling technology continue to push the boundaries of motion control and automation, providing solutions that address the evolving requirements of various industries.
Role of Encoder Couplings in Motion Control and AutomationAn encoder coupling is a crucial component in motion control and automation systems, used to facilitate precise position and speed sensing: It connects the shafts of a motor and an encoder, allowing the accurate transmission of rotational motion while maintaining precise alignment. The primary functions and usage of an encoder coupling include:
Overall, encoder couplings are essential for achieving accurate motion control and automation, enabling precise positioning and speed control in various applications such as robotics, CNC machines, conveyor systems, and more.
China Standard Customized Single Diaphragm Coupling, Coupling for Encoder with Low PriceProduct Description
Up Gold(ZheJiang )Automation Technology Co. Ltd, is a supplier of linear guide way, linear rail series,lead screw,block bearing, roller bearing ,ball bearing,pillow block bearing, rod ends bearing ,needle roller bearing,screw bearing ,slider bearings and slewing support bearings and so on. Quality is the life of enterprise. We are committed to improving the quality of our products and services. Advanced equipment, skilled technical workers, scientific testing instrument and strict quality control, all of these factors is the key to our development and growth in the intense market competition. Contact us now to realize the benefits of sourcing from our company. We insist to return new and old customers with best quality, fastest delivery time and most perfect after service. Your satisfaction is our goal.
Our Team:
We at Up Gold (ZheJiang ) Automation Technology Co. LTO. can offer unrivalled product and application knowledge, we can supply ballscrew products of any size or type to our valued customer.
*Two-year warranty, replace instead of repair. FAQ: Q: What is the producing process? A: Production process including raw material cutting, machine processing,grinding, accessories cleaning, assemble, cleaning, stoving, oil coating,cover pressing, testing, package. Q: How to control the products quality? A: Combining advanced equipment and strict management, we provide high standard and quality bearings for our customers all over the world. Q: What is the transportation? A: If small quantity, we suggest to send by express, such as DHL, UPS,TNT FEDEX. If large amount, by air or sea shipping. Q: How about the shipping charge? A: We will be free of domestic shipping charge from your freight forwarder in China. Q: Can you provide OEM service? A: Yes, we provide OEM service. Which means size, quantity, design,packing solution, etc will depend on your requests; and your logo will be customized on our products. Q: Could you tell me the delivery time of your goods? A: Generally it is 3-5 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to the quantity. Q: What about the packaging of your products? A: Normally we use standard commercial package, we also have our own brand packing or customized package as per customers’ requests. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Comparison of Encoder Couplings with Other Coupling TypesWhen comparing encoder couplings with other coupling types, such as flexible couplings and magnetic couplings, several key factors come into play: 1. Flexibility: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, offer flexibility to accommodate misalignment between the encoder and the driven component. They provide angular, radial, and axial flexibility, ensuring efficient signal transmission while minimizing stress on components. 2. Signal Transmission: Encoder couplings are specifically designed to ensure accurate signal transmission between the encoder and the controlled system. This distinguishes them from other couplings that prioritize torque transmission, such as magnetic couplings used for sealing applications. 3. Backlash Reduction: Encoder couplings often prioritize low backlash to enhance the precision and accuracy of motion control systems. While some other coupling types also aim to minimize backlash, encoder couplings excel in this aspect due to their primary function of accurate signal transmission. 4. Magnetic Couplings: Magnetic couplings are commonly used for torque transmission across a sealed barrier, such as in pump applications. While they offer the advantage of hermetic sealing, they may not be as suitable for precise signal transmission as encoder couplings. Magnetic couplings can also introduce a certain amount of backlash due to their design. 5. Torque Capacity: Flexible couplings and some other types of couplings are often selected based on their torque capacity to transmit power between shafts. Encoder couplings, on the other hand, prioritize signal integrity and precision, making them ideal for applications where accurate motion control is essential. 6. Application Focus: Encoder couplings are specialized for motion control and automation systems that require precise positioning and accurate signal feedback. Other coupling types may have broader applications, including torque transmission, vibration dampening, and sealing. 7. Maintenance: Encoder couplings, like flexible couplings, require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and accuracy. Magnetic couplings may have different maintenance requirements due to their sealing properties. Overall, encoder couplings stand out in their ability to facilitate accurate signal transmission and precise motion control. While other coupling types have their own advantages and applications, encoder couplings are specifically tailored to meet the demands of motion control and automation systems where maintaining signal accuracy is paramount.
Best Practices for Minimizing Electrical Interference in Encoder Coupling SystemsElectrical interference can adversely affect the performance and accuracy of encoder coupling systems. To minimize such interference and ensure reliable signal transmission, consider the following best practices:
Implementing these best practices will help minimize electrical interference and ensure that the encoder coupling system maintains accurate signal transmission, resulting in improved performance and reliability.
Choosing an Encoder Coupling: Key ConsiderationsWhen selecting an encoder coupling for a particular motion control or automation setup, several factors should be carefully considered: 1. Type of Misalignment: Identify the types of misalignment your system may encounter, such as angular, axial, or radial misalignment. Choose an encoder coupling that can effectively compensate for the specific misalignment your application might experience. 2. Torque and Load: Calculate the maximum torque and load that the coupling will need to transmit. Ensure that the selected coupling is rated to handle these loads without compromising performance or accuracy. 3. Backlash: Evaluate the allowable backlash based on the precision required for your application. Choose a coupling with minimal backlash to ensure accurate signal transmission. 4. Response Time: For applications requiring rapid changes in position or speed, select an encoder coupling with a low torsional stiffness. This enhances the response time of the system and ensures timely signal transmission. 5. Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment, including factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Choose a coupling material that can withstand the environmental conditions without degradation. 6. Shaft Size and Diameter: Ensure that the coupling is compatible with the shaft size and diameter of both the encoder and the driven component. Proper sizing prevents slippage and ensures efficient signal transmission. 7. Radial and Axial Runout: Evaluate the allowable radial and axial runout to prevent unnecessary stress on the coupling and encoder. Choosing a coupling that accommodates these factors contributes to a longer service life. 8. Space Limitations: If your setup has limited space, choose a compact and lightweight encoder coupling that can fit within the available dimensions without hindering other components. 9. Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the coupling material with both the encoder and the driven component. This is particularly important if the coupling will be exposed to chemicals or other substances. 10. Installation and Maintenance: Select a coupling that is easy to install and maintain. This helps reduce downtime during installation and ensures the longevity of the coupling. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the most suitable encoder coupling for your specific motion control or automation application, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy.
China factory Lt Series Rotary Encoder CouplingProduct Description
Flexible Coupling, High Quality Jaw Coupling Design feature: Basic Parameter And Main Dimension(GB/T4323-2002)
NOTE: Product Show
♦Other Products List
♦Our Company
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the design and manufacture of various types of coupling. There are 86 employees in our company, including 2 senior engineers and no fewer than 20 mechanical design and manufacture, heat treatment, welding, and other professionals. Advanced and reasonable process, complete detection means. Our company actively introduces foreign advanced technology and equipment, on the basis of the condition, we make full use of the advantage and do more research and innovation. Strict to high quality and operate strictly in accordance with the ISO9000 quality certification system standard mode. Our company supplies different kinds of products. High quality and reasonable price. We stick to the principle of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement and innovation to meet the customers” for the management and “zero defect, zero complaints” as the quality objective.
♦Our Services 2.Product Services 3.Samples Procedure 4.Research & Development 5.Quality Control ♦FAQ Q 2:Can you do OEM? Q 3:How long is your delivery time? Q 4: Do you provide samples ? Is it free or extra ? Q 5: How long is your warranty? Q 6: What is the MOQ? Q 7: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling ? Q 8: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order? Q 9: What’s your payment? ♦Contact Us
Materials Used in Manufacturing Encoder CouplingsEncoder couplings are manufactured using a variety of materials, each chosen for its specific properties and suitability for the intended application. Commonly used materials include: 1. Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offers good machinability. It is often used for encoder couplings in applications where weight reduction and moderate torque transmission are important. 2. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. It is commonly used in environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or harsh conditions is a concern. 3. Steel: Steel is robust and offers high strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications with higher torque requirements. It can be further treated for enhanced corrosion resistance. 4. Brass: Brass provides good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. It is often used in applications where electrical isolation between components is necessary. 5. Plastics: Various engineering plastics such as nylon, polyurethane, and PEEK (polyether ether ketone) are used in encoder couplings. These materials offer good wear resistance, low friction, and electrical insulation. 6. Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber is a lightweight, high-strength material known for its exceptional stiffness-to-weight ratio. It is used in applications where minimizing weight while maintaining rigidity is crucial. 7. Composite Materials: Composite materials combine different materials to achieve specific properties. They can offer a combination of strength, rigidity, and lightweight characteristics. The choice of material depends on factors such as the application’s requirements, environmental conditions, torque and speed specifications, and the need for electrical insulation or conductivity. When selecting the material for an encoder coupling, it’s essential to consider the mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties required for optimal performance and longevity.
Best Practices for Minimizing Electrical Interference in Encoder Coupling SystemsElectrical interference can adversely affect the performance and accuracy of encoder coupling systems. To minimize such interference and ensure reliable signal transmission, consider the following best practices:
Implementing these best practices will help minimize electrical interference and ensure that the encoder coupling system maintains accurate signal transmission, resulting in improved performance and reliability.
Key Functions and Benefits of Using an Encoder CouplingAn encoder coupling plays a vital role in motion control and automation systems, offering several functions and benefits: 1. Accurate Position and Speed Sensing: Encoder couplings ensure precise transmission of rotational motion between the motor and the encoder, allowing accurate measurement of position and speed. 2. Misalignment Compensation: They can accommodate angular, radial, and axial misalignments between the motor and encoder shafts, maintaining accurate motion even in imperfect alignment conditions. 3. Torsional Stiffness: Encoder couplings provide torsional rigidity to minimize torsional deflection, ensuring that the encoder’s output signals accurately reflect the actual motion of the motor. 4. Signal Integrity: By maintaining precise alignment, they prevent signal distortion or loss, leading to accurate position and speed feedback from the encoder. 5. Reduced Wear: Proper alignment reduces stress on shafts, bearings, and other components, prolonging the lifespan of both the motor and encoder. 6. Increased Efficiency: Encoder couplings help achieve smoother motion control, enhancing overall system efficiency and reducing the likelihood of jerky movements. 7. Enhanced Performance: With accurate position and speed feedback, encoder couplings contribute to improved system performance, consistency, and repeatability. 8. Flexible Design: They come in various designs and materials to suit different applications and requirements. 9. Compatibility: Encoder couplings are compatible with various motor and encoder types, making them versatile solutions for different setups. 10. Easy Installation: Most encoder couplings are designed for straightforward installation, reducing downtime during setup or maintenance. Overall, encoder couplings are essential components that ensure precise motion control, accurate position sensing, and reliable automation in various industries and applications.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||